Business analysis techniques are a structured and systematic approach to identify new opportunities, optimize costs, pinpoint issues, evaluate potential fixes, and streamline operations. In modern-day business, this has become an essential process for organizations that wish to ensure that the business analysis is thorough and aligned with organizational objectives. Therefore, firstly a company must recognize its areas of weakness and thereupon consider potential remedies to strengthen them. That’s precisely the situation where business analysis is useful. Additionally, it supports in making key decisions to enhance the effectiveness of the company’s day-to-day operations.
What is The Significance of Business Analysis?
- By carefully analyzing consumer input and market trends, it assists businesses in identifying their needs and further offers strategies for coordinating those demands with their overarching goals.
- By implementing techniques like gap analysis and process mapping, one can greatly enhance and optimize processes, thereby contributing to the enhancement of corporate operations’ overall efficiency.
- Above all, by applying Data Analysis to forecast potential threats and challenges it not only reduces risks for businesses but also provide solutions for overcoming them.
Top 10 Business Analysis Techniques
The most common Top 10 Business Analysis Techniques used by modern-day business analysts are:
1. SWOT Analysis
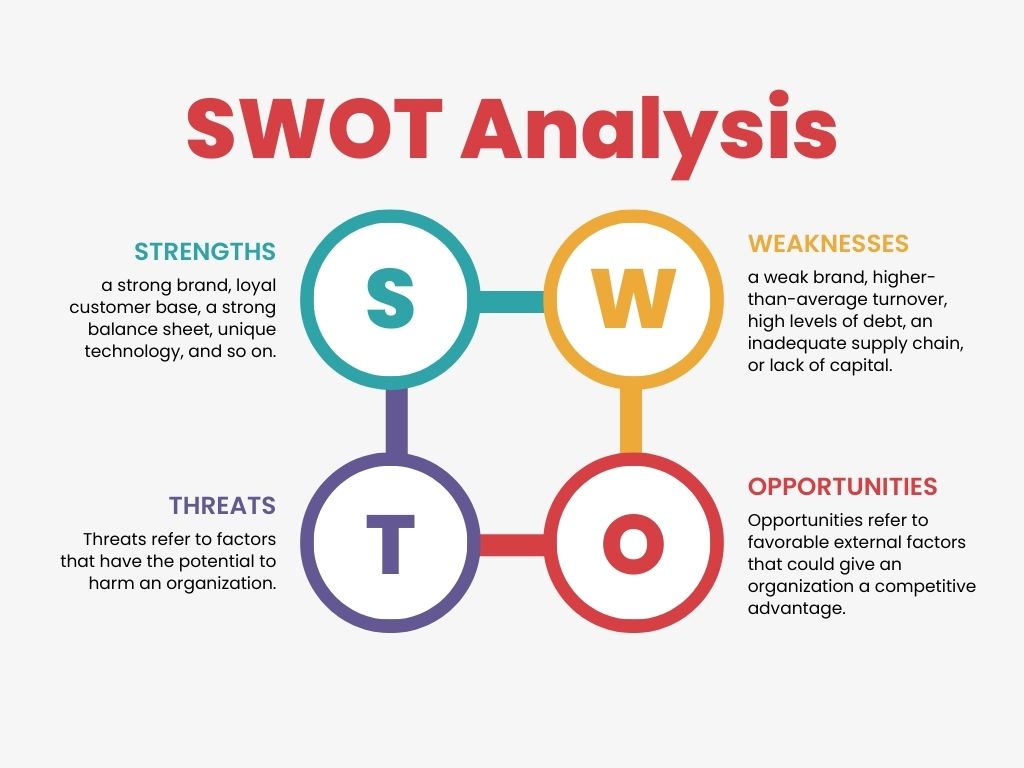
One of the most frequently used business analysis techniques is SWOT. It takes into account both internal and external elements, including dangers and opportunities as well as advantages and disadvantages.
- Strength: qualities of a business that give it an edge over competitors. These include the company’s standing, brand value, and staff loyalty.
- Weakness: A company’s traits that might make it less competitive than rivals. E.g. bad management and internal strife.
- Opportunities: The company can seize any external circumstances or elements. For example, an unexplored market niche, press coverage, etc.
- Threats: Any outside force that might hinder a project or cause issues for the company or its expansion and success. E.g. A weak economy, supply chain disruption, etc.
2. Business Processing Model (BPM)
Business Process Modeling (BPM) serves as a technique to visualize business process analysis and augment productivity. It comprises of process’s main steps, inputs, outputs, and stakeholders before visualizing the whole flow of the process.
The process owner creates a process flow diagram based on the goals and scope of the process, along with the main tasks. This will highlight the phases of the process, decision points, and feedback loops.
By employing business process modeling, organizations may find areas for operational improvement as well as bottlenecks along with inefficiencies. Moreover, it creates the foundation for automation and process optimization, which reduces costs and increases production.
3. MOST Analysis
The MOST analysis establishes the company’s mission, objectives, and strategy for achieving them. This helps to clarify the capabilities and goals of the company.
MOST = Mission, Objectives, Strategy, and Tactics
- Mission: It outlines the objective the company seeks to accomplish. Clarity regarding the mission is equally important for the analysis of the following variables. The authorities should reevaluate the mission to determine its success or effectiveness.
- Objectives: This describes the goals that every department will work toward to accomplish the company’s mission.
- Strategy: This describes the plan a business must take to achieve its objectives. Utilizing any range of tactics is permissible if they contribute to accomplishing the objectives. Rethinking the implemented approach is necessary if it is not yielding the desired results.
- Tactics: These distinct and targeted techniques come together to produce a comprehensive plan. So, Strategies should be simple to implement and provide participants with unambiguous instructions.
4. PESTLE
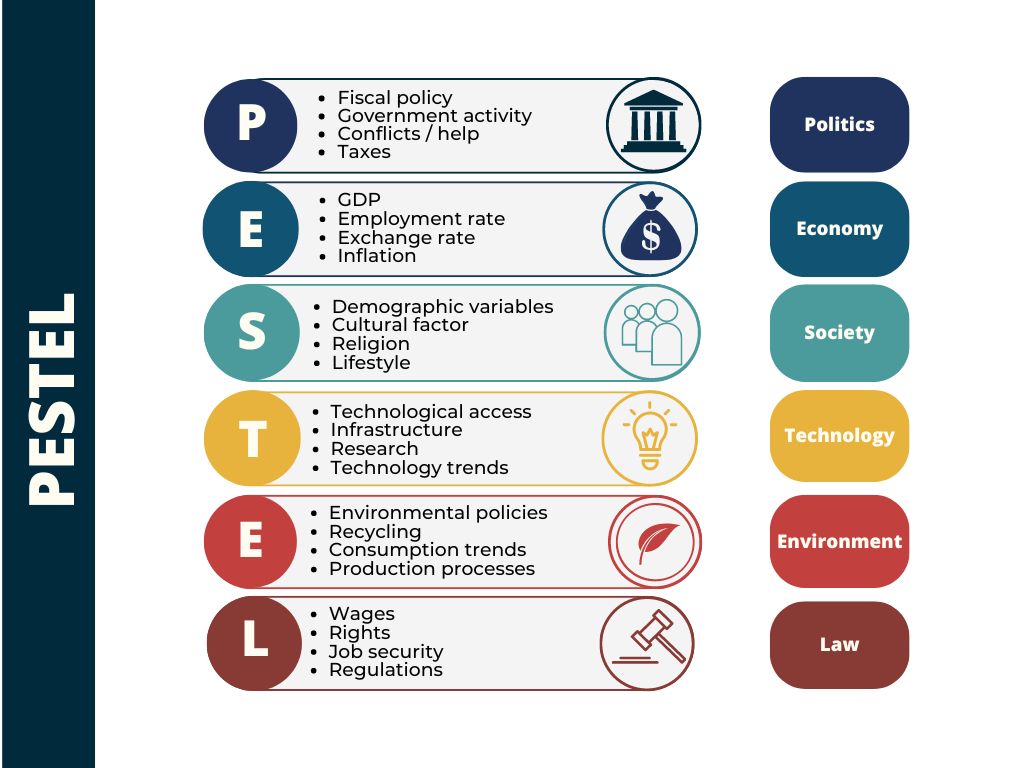
Unlike other methods, PESTLE identifies and investigates only external factors that may impact an organization.
- Political: Political factors like government rules and policies affect business.
- Economic: Economic factors, such as interest rates, labor costs, oil prices, and inflation rates, can directly impact a company’s profitability.
- Social: Sociological components consider social and cultural trends that might affect business.
- Technological: The term “technological variables” refers to developments in IT and communication that might have an impact on business.
- Legal: Legal considerations are the rules and laws that a company has to abide by.
- Environmental: Environmental factors consider how the business is affected by the environment.
Based on the findings of each of these elements, an analyst may find opportunities and challenges and further its strategy.
5. CATWOE
The CATWOE approach delivers a methodical structure for analyzing and fixing complicated issues.
- Customers: customers are the people who are impacted by this issue or choice.
- Actors: The people who are responsible for executing the process of change are the actors.
- Transformation Process: The transformation process is the set of actions and methods required to convert input into output.
- Worldview: This highlights the objectives and purpose for the company’s establishment and makes reference to the principles and values that the stakeholders support.
- Owners: individuals or groups who are decision makers in the company.
- Environmental Constraints: External constraints are the imposed limits that may affect the issue or choice.
6. Brainstorming
This is one of the easiest business analysis methods for generating a ton of original group ideas to solve issues or achieve objectives. Teams and individuals are encouraged to express their thoughts honestly and without concern for the consequences.
The ideas generated from a brainstorming session help business analysts look into possible solutions to the problems they have discovered. Brainstorming is a helpful technique because it generates novel concepts and creative solutions that are not typically considered. These ideas serve as the starting point for further investigation and analysis, enabling improvement and implementation.
7. The 5 whys
The Five Whys, a business analysis technique, enables the definition of an issue and also the identification of its underlying causes. This is equivalent to asking why a specific situation happened five times. Asking “why” questions several times is necessary to identify the source of the issue. By doing so, you may deal with the problem’s root cause as opposed to just its symptoms.
This form of business analysis can help identify the reasons for a project’s delay or a particular process’s malfunction. Furthermore, finding the root cause of the issue might help find a practical solution that addresses the issue and prevents it from happening again.
8. Use Case Modeling
A business analysis technique called use case modeling explains how people utilize technology to accomplish a certain objective or result. It comprises figuring out every scenario or course a user may take while using the technology and recording these exchanges.
With the use of this business analysis technique, you can ascertain the needs of the system, spot any problems, as well as make sure the system is built to meet user desires. It helps ensure that the final product is user-friendly and produces the intended outcomes.
9. MoSCoW
This technique called the MoSCoW approach, ranks demands and features according to importance. It is certainly a useful tool for Business Analysts because it helps rank requirements according to their significance for achieving business objectives.
Must or Should, Could or Wouldn’t is referred to as MoSCoW.
a) In order to achieve company goals, we prioritize needs that are essential to the project’s success and consider them non-negotiable.
b) The non-urgent nature of the should-have criteria allows for their postponement. Also, if time and resources allow, it is advisable to include these elements, despite their lesser importance compared to the must-have elements.
c) Desirable but not necessary for the project or product to succeed are could-have needs. Although, they are not essential to the company’s goals, these factors are considered when time and resources permit.
d) Requirements that are deemed superfluous and excluded from the product are basically those that won’t have them.
10. Mind Mapping
Mind mapping is a visual method for prioritizing and organizing ideas or data. It involves creating a non-linear graphic that links several ideas or concepts. Mind maps frequently structure themselves around a fundamental thought or topic, which then expands into associated concepts or subtopics.
This technique makes it possible to see complicated data in a way that is simple to comprehend. Applications for mind mapping in business include requirement gathering, process mapping, and project planning. Also, it makes it possible to comprehend a problem or circumstance more thoroughly and promotes improved stakeholder engagement and communication.
Become a Certified Business Analyst – Henry Harvin Business Analyst Course.

About the course:
In this Business Analyst Certification Course explore, Analyze, Solve Business Problems using Analytical tools like Python and Advanced Excel. Skills Covered: Data Visualization, Data Modeling, String Function, Mathematical Function, Data Blending and Data Mapping. Henry Harvin gives the facility to undergo various projects along with the course, guaranteed internship, and placement support. Plus, Lifetime support and access, 24X7 lifetime free upgrade.
Professional Certificate in Business Analyst Course Fees
The fee for this Business Analyst Course is Rs. 89000/-
Conclusion
Gaining proficiency in these ten strategies will not only enable you to succeed in your organization but also manage the dynamic business environment and outperform the competition. Whether you are an experienced professional or a budding analyst, applying these tactics will enable you to take on challenging problems, provide creative answers, and promote long-term success.
Must Reads:
- Complete Guide To Business Intelligence Analyst: To Make You Successful
- Business Intelligence And Business Analytics The New Buzz Words in 2024 [Updated]
- What is Business Analytics? Course Details, Syllabus, and Jobs
- The Best Online Business Analytics Courses for Beginners: 2024
- Business Analyst Job Descriptions: Salaries and Skills for 2023
FAQs
Q1. Why is Business Analysis important?
A. In Business analysis, we use tools and methods to deliver value to stakeholders. By doing so, it helps businesses determine their requirements and needs. Making decisions in view of information can assist you with staying in front of the opposition in the present high-speed business climate.
Q2. What are business analytical techniques?
A. The techniques used to think up and carry out the procedures fundamental for recognizing an organization’s necessities and come by the best outcomes are known as business analytical techniques. In addition, these methods help in identifying key areas of improvement and developing effective strategies to achieve organizational goals. There is no “one size fits all” system in light of the fact that each business or association is unique.
Q3. What are the three main techniques of business analysis?
A. The three main techniques are:
- SWOT
- PESTLE
- Business process modeling
Q4. What is the main role of business analysis?
A. Additionally, business analysts are tasked with identifying key stakeholders, analyzing market trends, and collaborating with cross-functional teams. It calls for a thorough grasp of systems, including how they work, who must be engaged, and how to get everyone on board.
Q5. How to become a Business Analyst?
A. The cycle to turning into a business expert is fairly straightforward. First of all, it requires a four-year certification. In addition, a couple of long periods of expert experience are required. Furthermore, following that, you can choose whether assuming a business examiner confirmation or a graduate degree is the best strategy for your calling.







Your writing is both engaging and relatable.
Your insights always leave me thinking.
Your blog is a breath of fresh air in the crowded online space. I appreciate the unique perspective you bring to every topic you cover. Keep up the fantastic work!
Thank you